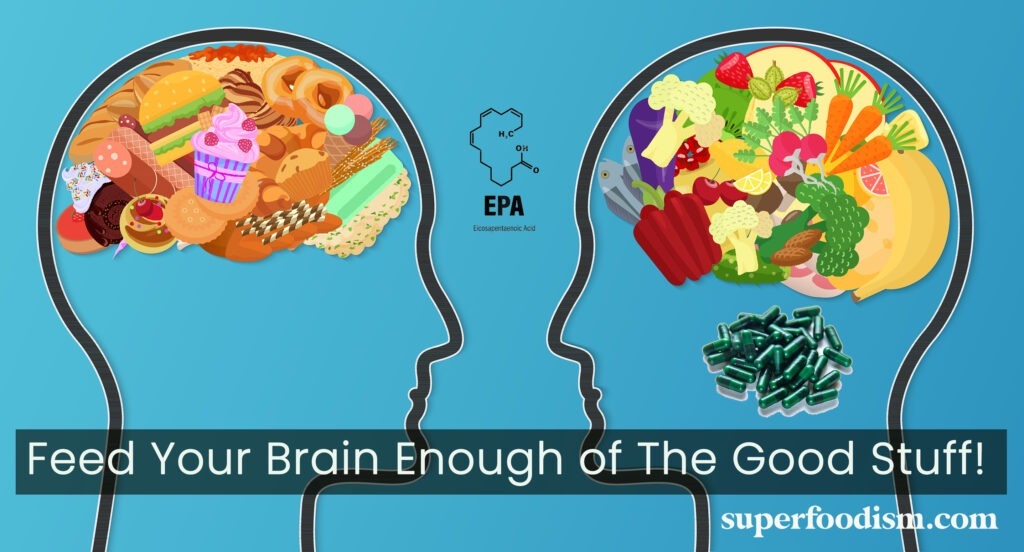
The Profound Benefits of EPA for Brain Health and Mood Enhancement
In the quest for optimal well-being, the profound influence of nutrition on cognitive function and emotional balance has emerged as a pivotal focus of scientific inquiry. Among the many nutrients that play a crucial role in supporting brain health, Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid, stands out as a remarkable contributor. This article explores the multifaceted benefits of EPA for the brain, mood, and cognitive function, shedding light on the pivotal role this nutrient plays in our mental and emotional well-being.
The Brain’s Best Friend: EPA and Cognitive Function
EPA, a polyunsaturated fatty acid, is renowned for its neuroprotective properties. Scientific studies have consistently demonstrated the positive impact of EPA on cognitive function. One of the key ways in which EPA supports the brain is by promoting healthy cell membranes. As a crucial component of cell membranes, EPA contributes to their flexibility and fluidity, facilitating efficient neurotransmission and signal transduction.
Furthermore, EPA has been linked to increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein vital for the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons. Higher levels of BDNF are associated with improved learning, memory, and overall cognitive performance. In essence, EPA acts as a cognitive enhancer, fostering an environment conducive to optimal brain function.
EPA and Mood Regulation:
The influence of EPA extends beyond cognitive function to the intricate realm of mood regulation. A growing body of research suggests a strong correlation between omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA, and mental well-being. EPA is known to modulate the production of neurotransmitters, including serotonin and dopamine, which play pivotal roles in mood regulation.
Studies have demonstrated that individuals with higher levels of EPA are less likely to experience symptoms of depression and anxiety. The anti-inflammatory properties of EPA further contribute to its mood-stabilizing effects, as inflammation has been linked to mood disorders. By mitigating inflammation, EPA creates an environment in which the brain can function optimally, fostering emotional resilience.
EPA and Neuroinflammation:
Neuroinflammation, characterized by the activation of immune cells in the brain, is a key factor in various neurological disorders. EPA’s anti-inflammatory properties make it a potent ally in the battle against neuroinflammation. Chronic inflammation has been implicated in the development of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, and EPA’s ability to quell inflammation showcases its potential in preventing or mitigating these conditions.
Additionally, EPA’s role in supporting the production of anti-inflammatory molecules, such as resolvins and protectins, further contributes to its neuroprotective effects. By promoting a balanced inflammatory response, EPA helps safeguard the brain from the damaging effects of chronic inflammation, thereby preserving cognitive function.
EPA and Neuroplasticity:
Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself, is crucial for learning, memory, and overall cognitive flexibility. EPA has been shown to enhance neuroplasticity by promoting the growth and branching of dendrites, the extensions of nerve cells involved in transmitting signals. This structural enhancement contributes to the brain’s ability to form new connections and adapt to changing circumstances.
As individuals age, cognitive decline becomes a concern for many. The neuroprotective properties of EPA make it a promising candidate for preventing or delaying cognitive decline. Research suggests that higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA, are associated with a reduced risk of cognitive impairment and dementia in older adults. By preserving neuronal structure and function, EPA serves as a guardian against age-related cognitive decline.
Practical Strategies for Incorporating EPA into Your Diet:
Given the myriad benefits of EPA for the brain, incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet becomes a strategic step toward promoting cognitive health. Traditionally good sources have been fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as they are excellent sources of EPA. The problem with fish these days is that it’s heavily contaminated. Because of this, here in The Netherlands, recommendations are even against eating fish more than 3 times a week.
Alternatively, high-quality algal oils and of course, Marine Phytoplankton are available for adequate daily Omega-3 intake without the concern of environmental pollution and pressure on diminishing fish populations.

So….
In the fascinating realm where nutrition intersects with neuroscience, EPA emerges as a shining star, showcasing its prowess in supporting cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall brain health. From bolstering neuroplasticity to mitigating neuroinflammation, the multifaceted benefits of EPA underscore its significance as a vital nutrient for the mind.
As we delve deeper into understanding the intricate connection between nutrition and brain function, EPA stands as a beacon of hope, offering a natural and accessible means to fortify our cognitive resilience. Embracing a diet rich in EPA-rich foods or considering supplements under the guidance of healthcare professionals opens the door to a brighter, more vibrant cognitive future—one where the marvels of EPA contribute to a life lived at its cognitive and emotional zenith.










0 Comments